디자인패턴
[Java][디자인 패턴] 9. 복합체 패턴 (Composite Pattern)
복합체 패턴은 객체 간의 계층적 구조화를 통해 객체를 확장하는 패턴이다. 복합체는 재귀적으로 결합된 계층화된 트리 구조의 객체이다.
복합 객체란?
- 복합 객체는 객체가 또 다른 객체를 포함하는 것
- 복합적인 객체 관계를 복합화 또는 집단화라고 한다.
- 강력한 결합 구조를 가진 상속과 달리 느슨한 결합을 가지고 있으며, 의존체 주입 방식을 사용한다.
복합체 패턴이란?
- 복합채 패턴은 분할 디자인 패턴의 하나이다.
- 복합체 패턴을 이용하면 객체의 상위, 하위 체계를 파악할 수 있고 일대일, 다대일을 처리하는 데도 매우 유용하다. 하나의 객체를 호출하면 서브로 갖고 있는 자식의 객체 메서드를 호출할 수도 있다.
복합체 패턴은 언제 사용하면 좋을까?
트리 모양을 가진 구성 요소들
- 회사와 부서, 팀과 같이 그룹과 해당 그룹에 속한 하위 그룹이 있는 계층(트리) 구조 형태의 관리
- 세트 상품 (다른 세트 상품의 일부가 될 수 있음)
- 회원 관리, 이메일 전송 (그룹으로 묶인 회원을 대상으로 메일을 보낸다)
- 폴더와 파일 구조와 같은 트리 형태
- 파워포인트의 도형 그룹, 여러 도형을 한꺼번에 바꿀 경우
복합체 패턴의 구성 요소
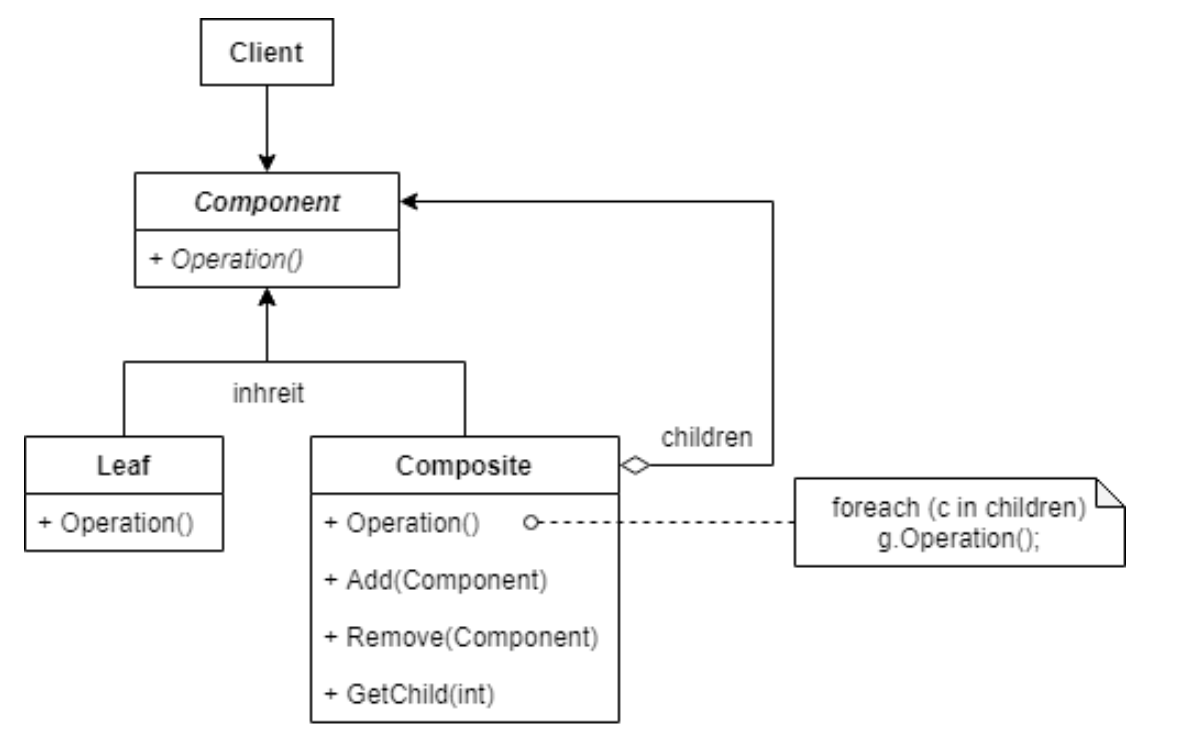
- Component
- 컴포넌트 역할을 수행하는 추상 클래스
- 노드인 Composite와 마지막 노드인 Leaf에 공통으로 적용된다.
- Composite와 leaf는 동일한 처리를 위해 Component 추상 클래스를 상속받는다.
- Composite
- 복합체 패턴은 다른 복합체 패턴을 포함할 수도 있고 마지막 노드가 될 수도 있다
- Leaf
- 복합체는 계층적 트리 구조로 되어있다
- 노드의 제일 마지막 객체
- Client
- 복합체를 호출하는 클래스
복합체 패턴 예제 코드 구조
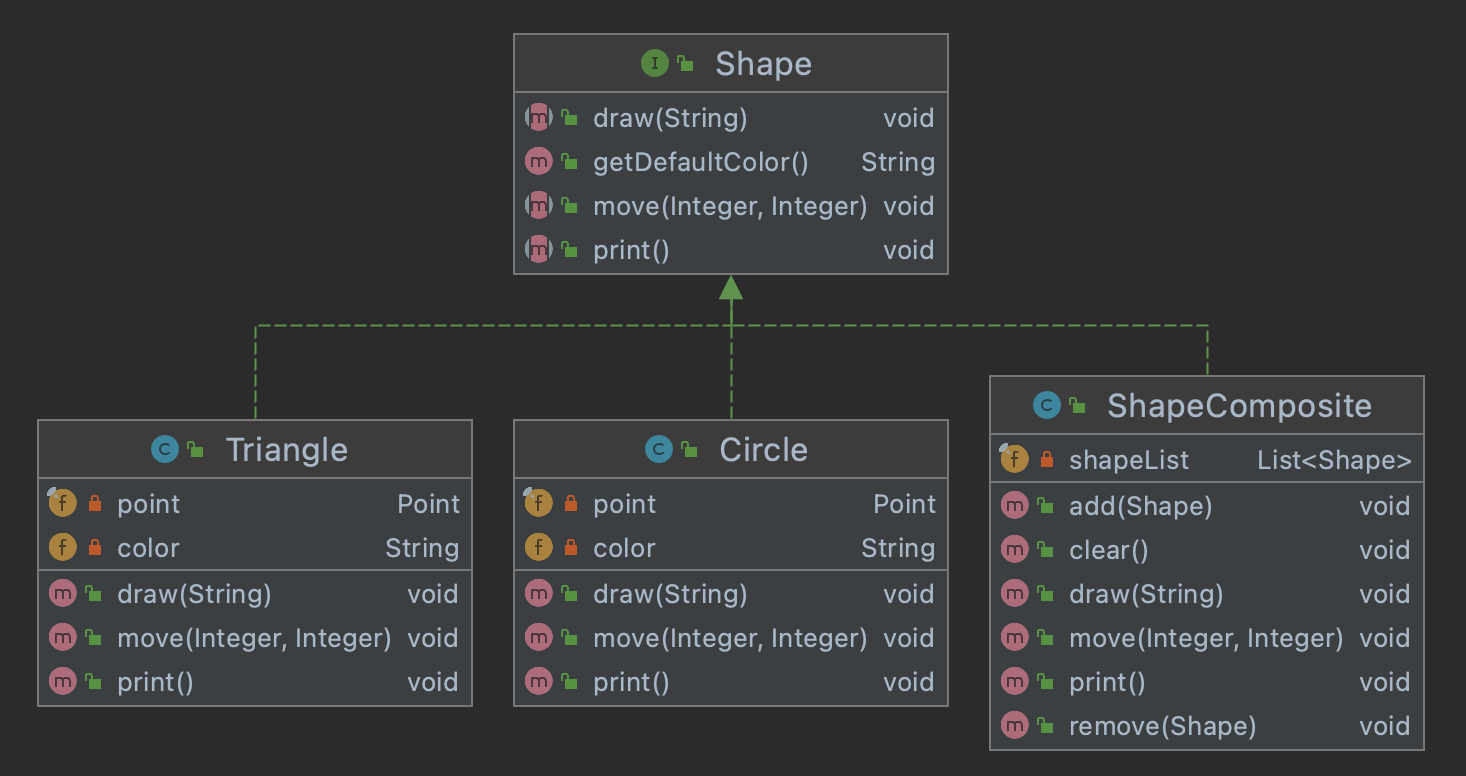
- Component - Shape 클래스 (Leaf와 Composite에 공통으로 적용할 클래스)
- Composite - ShapeComposite (Shape List를 가지고 그룹 전체에 공통된 연산을 적용할 클래스
- Leaf - Triangle, Circle (Component를 구현하고 있는 공통적인 동작을 수행하는 Leaf 클래스)
- Client - TestCode
복합체 패턴 구조에 해당하는 예시 코드로는, 도형의 색을 변경하고 옮기고 표현하는 공통적인 동작을 수행하는 Shape 인터페이스를 만들고, 각 도형들을 그룹화해서 관리할 수 있는 ShapeComposite 클래스를 통해 객체를 관리해보려 한다.
복합체 패턴 코드
1. Shape 인터페이스
public interface Shape {
void draw(String fillColor);
void move(Integer x, Integer y);
void print();
default String getDefaultColor() {
return "BLUE";
}
}2. Shape 인터페이스를 구현하고 있는 Circle, Triangle 클래스
public class Circle implements Shape {
private final Point point;
private String color;
public Circle() {
this.point = new Point();
this.color = getDefaultColor();
}
@Override
public void draw(String fillColor) {
this.color = fillColor;
}
@Override
public void move(Integer x, Integer y) {
point.move(x, y);
}
@Override
public void print() {
System.out.println("[Circle][" + color + "] " + point.toString());
}
}public class Triangle implements Shape {
private final Point point;
private String color;
public Triangle() {
this.point = new Point();
this.color = getDefaultColor();
}
@Override
public void draw(String fillColor) {
this.color = fillColor;
}
@Override
public void move(Integer x, Integer y) {
point.move(x, y);
}
@Override
public void print() {
System.out.println("[Triangle][" + color + "] " + point.toString());
}
}3. Shape의 좌표 값을 가지고 있는 Point 클래스
public class Point {
private Integer x;
private Integer y;
public Point(Integer x, Integer y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
public Point() {
this.x = 0;
this.y = 0;
}
public void move(Integer x, Integer y) {
this.x = this.x + x;
this.y = this.y + y;
}
public Integer getX() {
return x;
}
public Integer getY() {
return y;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Point{" +
"x=" + x +
", y=" + y +
'}';
}
}4. Shape들을 그룹화해서 한꺼번에 관리하는 ShapeComposite 클래스
public class ShapeComposite implements Shape {
private final List<Shape> shapeList = new ArrayList<>();
@Override
public void draw(String fillColor) {
for (Shape shape : shapeList) {
shape.draw(fillColor);
}
}
@Override
public void move(Integer x, Integer y) {
for (Shape shape : shapeList) {
shape.move(x, y);
}
}
@Override
public void print() {
for (Shape shape : shapeList) {
shape.print();
}
}
public void add(Shape shape) {
shapeList.add(shape);
}
public void remove(Shape shape) {
shapeList.remove(shape);
}
public void clear() {
System.out.println("clear");
shapeList.clear();
}
}5. ShapeComposite 클래스의 테스트 코드
class ShapeCompositeTest {
@Test
@DisplayName("도형을 그리고 한꺼번에 옮긴다")
void drawShape() {
Shape triangle = new Triangle();
Shape triangle2 = new Triangle();
Shape circle = new Circle();
ShapeComposite shapeComposite = new ShapeComposite();
shapeComposite.add(triangle);
shapeComposite.add(triangle2);
shapeComposite.add(circle);
shapeComposite.print();
shapeComposite.draw("RED");
shapeComposite.print();
shapeComposite.move(1, 1);
shapeComposite.print();
shapeComposite.move(2, -3);
shapeComposite.print();
}
}결과 값
[Triangle][BLUE] Point{x=0, y=0}
[Triangle][BLUE] Point{x=0, y=0}
[Circle][BLUE] Point{x=0, y=0}
[Triangle][RED] Point{x=0, y=0}
[Triangle][RED] Point{x=0, y=0}
[Circle][RED] Point{x=0, y=0}
[Triangle][RED] Point{x=1, y=1}
[Triangle][RED] Point{x=1, y=1}
[Circle][RED] Point{x=1, y=1}
[Triangle][RED] Point{x=3, y=-2}
[Triangle][RED] Point{x=3, y=-2}
[Circle][RED] Point{x=3, y=-2}복합체 패턴의 장점과 단점
장점
- 단일 객체와 복합 객체 (그룹)을 동일하게 여기기 때문에 묶어서 연산하거나 관리할 때 편하다
- 객체에 따라 다르게 처리하지 않고 동일하게 취급해야 할 때 사용
- 투명성을 이용해 클라이언트 사용을 단순화할 수 있음. (if문을 사용하지 않고도 Composite와 Leaf를 판단 가능)
단점
- 재귀 호출의 특징 상 트리의 Depth가 길어질수록 라인 단위의 디버깅에 어려움이 생긴다.
- 복합체 패턴은 수평적, 수직적 모든 방향으로 객체를 확장할 수 있으나 수평적 방향으로만 확장하도록 Leaf를 제한한 Composite를 만들기는 어렵다.
Github 코드
참고 자료
1.쉽게 바로 써먹는 디자인 패턴 책
http://www.yes24.com/Product/Goods/93173296
쉽게 배워 바로 써먹는 디자인 패턴 - YES24
객체지향 프로그래밍 설계 원칙, 패턴을 알면 개발이 보인다디자인 패턴은 어느 날 갑자기 생겨난 방식이 아니다. 객체지향 개발 과정에서 겪는 다양한 이슈를 종합해보면 서로 비슷한 유형의
www.yes24.com
'개발 > 디자인패턴' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Java][디자인 패턴] 11. 파사드 패턴 (Facade Pattern) (0) | 2022.03.12 |
|---|---|
| [Java][디자인 패턴] 10. 장식자 패턴 (Decorator Pattern) (0) | 2022.03.09 |
| [Java][디자인 패턴] 8. 브리지 패턴 (Bridge Pattern) (1) | 2022.03.07 |
| [Java][디자인 패턴] 7. 어댑터 패턴 (Adapter Pattern) (0) | 2022.03.06 |
| [Java][디자인 패턴] 6. 프로토타입 패턴 (Prototype Pattern) (0) | 2022.03.05 |